By Saravana Kumari Sundaram, Director – Insurance Solutions, Virtusa
Now, the data can also be used by insurers to transform business processes like digital marketing, Sales Force Automation (SFA), self-service channels and virtual agents.
The four drivers behind digital transformation
There are several factors contributing to the growth of big data, cloud and use of artificial intelligence in insurance. These include:
-
Legacy Modernisation: Insurers are moving towards cloud as they revamp legacy systems, e.g. policy administration and claims processing systems; opting for mobile enabled, digital solutions that are embedded with analytics.
-
Operational Efficiency: Insurers are under pressure to increase operational efficiencies, thanks in part to the economic downturn, coupled with demographics and social factors. For example, life insurers are faced with longer-living customers, which affects the products and services they offer them.
-
Customer Experience: Insurance has moved from a policy centric to a customer centric world. Digital channels, social reputation and the rise of millennials as customers and employees are changing the way insurers market and sell products and services. IDC predicts that marketing heads will collectively spend US$6.6 Billion in 2015 to enhance the total customer experience across all channels.
-
Digital Transformation: The growth in the use of mobile devices, telematics, sensors and the IoT, along with social and location data, are increasing the amount of data gathered. Insurers are being challenged to collect and analyse this real-time data. This is transforming core processes such as policy administration, claims management, regulatory compliance and customer service.
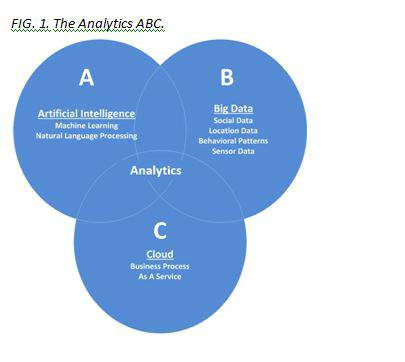
The ABC of analytics use
- A is for Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the big brother of cloud and big data. AI is having a growing impact on business processes and decision making as machine learning processes, neural networks, intelligent analytics and natural language processing become embedded in insurers systems.
- B is for Big Data: IDC predicts that big data and analytics spending will increase to US$125 Billion in 2015. Contemporary customers are more open to being monitored if there is a significant advantage in pricing or service; for example, telematics is disrupting the business model of auto-insurance with PAYD (Pay-As-You-Drive) and PHYD (Pay-How-You-Drive) pricing mechanisms being introduced.
- C is for Cloud: Needless to say, with the sheer volume of data comes the need for cloud, due to increasing data storage requirements. As insurers grow the data banks they hold, cloud will be the answer to their needs for elasticity. Cloud will also provide the computing power and capacity required to apply advanced analytics to the data that insurers hold.
Through analytics – AI, big data and cloud have become woven together. Analytics is opening up new opportunities in the insurance business across multiple processes and lines of business. One such area is pre-sales and marketing, where insurers now have the ability, through a consolidated single view of a customer, to understand them better than ever before; and so retain them, up-sell or cross-sell with much more ease. Analytics is also supporting new business and underwriting, with the capability to make product suggestions based on demographics, behavioral analytics and historical data, ultimately making insurers more profitable.
Finally, customer service and customer interactions are greatly improved through the use of analytics. For example, call-centre analytics can identify the common issues that customers are calling with, and ensure ‘fixes’ for these issues are provided by self-service options. This reduces the number of unhappy customers contacting a call-centre and ensures customers with other queries can speak to a customer service agent when they need to.
AI, big data and cloud, combined with huge volumes of unstructured big data that fuel decision-making are drastically changing the insurance industry. Insurance, an industry which began in a coffee shop, is undergoing an incredible digital transformation. As the ‘ABC’ of analytics becomes more commonplace in the insurance industry, there is a sense we are just touching the tip of the iceberg. The future for the insurance industry, if it continues to embrace digital transformation, is very bright indeed.
|