By Towers Watson
Predictive Modelling: A Tool for Better Understanding Insured Risks
P&C insurers use predictive modelling techniques to enhance their understanding of both current and future insured risks. This knowledge has led to improved risk segmentation, underwriting, pricing, claim and marketing decisions. For example, auto insurance carriers have begun differentiating liability coveragecosts by symbol, which historically has not been considered at all in bodily injury rating. Likewise,homeowners data show a clear interaction between territorial relativities and individual perils (i.e., thedifference in relative risk between territories varies depending on the peril being evaluated). Traditionalpricing techniques typically do not quantify this interaction between risk parameters, but a predictivemodel will adjust for this and other interactions, enabling the insurer to develop premiums that moreaccurately reflect the relative risk characteristics of the pool of underlying policyholders.
Detailed Findings
Predictive Modelling Proves Its Worth…
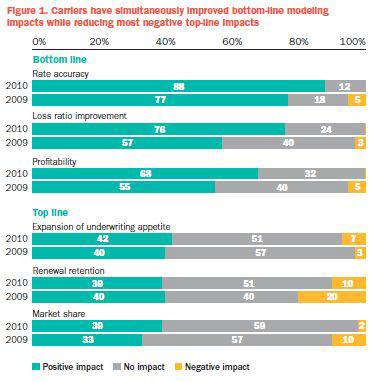
As they realize the value of predictive modelling, P&C insurers are expanding their applications and investing more in predictive modelling tools. The 43 U.S. companies that responded to both the 2010 and 2009 surveys reported significant increases in rate accuracy, improvements in loss ratio and profitability growth. Their current use of predictive modelling is up roughly 10% across all lines of business compared to 2009. These respondents also reported that predictive modelling has helped expand their company’s underwriting appetite, and a significant percentage said it helped increase market share (Figure 1).
…and Companies Increase Their Use…
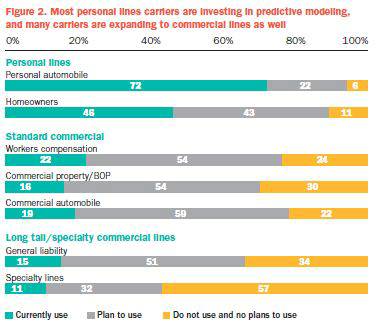
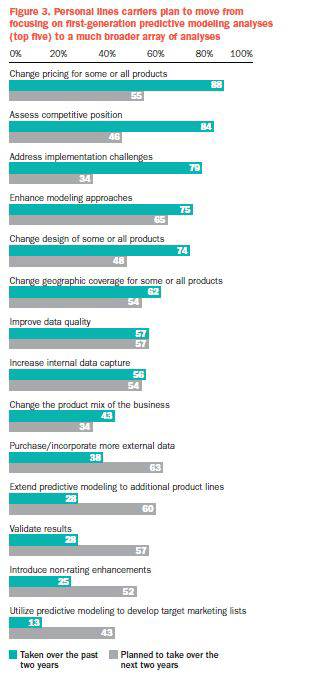
As the approach delivers greater value, companies are expanding their use of predictive modelling. Personal lines carriers, with their large volume of homogeneous data, high frequency and low severity, are leading the way, with 94% of those respondents saying they currently use or plan to use the technique for personal auto and 89% saying they use or will use it for homeowners.U.S. personal lines carriers plan to move beyond first-generation predictive modelling to a much broader array of analyses. Comparing actions taken by carriers over the past two years to those planned for the next two years, there is now much more emphasis on validation of results, data (both in terms of increasing internal data capture and incorporating more external data), extension of predictive modelling to additional lines, introduction of non-rating enhancements and applications in target marketing (Figure 3).
Commercial lines carriers are also adopting predictive modelling techniques. Roughly 20% of respondents use predictive modelling for workers compensation, commercial property or auto, but well over half of commercial lines respondents say they plan to apply it more aggressively in the future (Figure 2).
U.S. small commercial carriers have had a strong focus on pricing over the past two years. Their future plans are ambitious, with data quality/availability and enhancement of modelling approaches receiving primary emphasis among a broad list of priorities over the next two years. While general liability carriers are among the last to come on board (as expected because of the low-frequency/high-severity nature of the coverage), many plan to adopt the use of predictive modelling techniques.
U.S. commercial large account/specialty carriers have focused primarily on product pricing, but many plan to expand their focus across multiple dimensions. As is the case for personal lines and small commercial lines, data quality and availability will be key areas of focus over the next two years.
In addition, 63% say they will extend predictive modelling to additional product lines, while 74% say they will enhance modelling approaches.
…and Modelling Sophistication as Well
Carriers are finding that effective implementation of predictive modelling enhances risk selection and pricing, leading to greater profitability and potential market share growth. The benefits are clear enough that insurers are moving ahead with implementation and broader use of the techniques. Although personal lines carriers are currently more aggressive than their commercial lines counterparts across many dimensions, commercial lines carriers recognize the value and plan to broaden their use of predictive modelling in the near future. Innovative model enhancements continue to be developed and adapted to specific company needs, applying further competitive pressure on slow adopters. New predictive modelling applications will necessitate a sophisticated approach as companies aggressively move forward to develop and implement new applications.
Predictive Modelling Techniques:
What’s Hot
Price optimization and the use of telematics technology is growing, although at a slower pace for smaller carriers. They nonetheless expect to implement these techniques in the next two years. Here is a summary of respondents’ use of the top new techniques:
Price Optimization. Price optimization is commonly used by national personal lines carriers. It is used much less by smaller carriers, although a majority of them say they plan to adopt it within the next two years. Advanced predictive modelling techniques such as price optimization pose challenges, including insufficient data for building customer demand models — carriers’ top optimization implementation concern. Two-thirds of personal lines respondents indicated that lack of data is one of their three top concerns, and it is an issue for two thirds of small to midsize commercial lines carriers as well. Less than half of larger commercial carriers and specialty carriers view it as a major hurdle. Regulatory restrictions on implementation of pricing structures based on optimization techniques ranked second as a barrier for personal lines, followed by lack of systems expertise and inadequate Regulatory concerns are not limited to just the more advanced applications, however. While respondents say they have not encountered significant challenges in gaining regulatory approval of pricing predictive models, keeping their scoring algorithms proprietary has been more problematic.
Telematics. Only a minority of carriers expect to use telematic information for pricing, but those that do plan to use it anticipate implementing a wide variety of applications over the next two years, particularly in commercial lines. The relative ease and additional value of capturing telematic data in commercial fleets is likely spurring the interest by commercial lines carriers. There are many different ways that the use of telematic technology is referred to, including pay as you drive (PAYD) and usage-based insurance (UBI). Currently being adopted by many auto insurers, telematics is the technology of sending, receiving and storing information via telecommunications devices in vehicles. Multiple times per second, telematic devices record information such as location (if the device includes GPS capability), speed, braking time, mileage, and day and time the vehicle is used. The technology has numerous applications, including enhanced claim cost reduction through driver feedback, improved customer service and the ability to attract better risks. Perhaps most important, using telematic data, auto insurers can also set premiums based on actual driving experience.
Competitive Market Analysis (CMA).Most carriers perform some type of competitive analysis, but only a minority of carriers currently prepares detailed qualitative or quantitative analyses across their books of business to fully understand the competitive landscape. Nonetheless, solid CMA is increasingly important in aligning pricing by line of business.
Claim Applications. Within two years, nearly half of responding carriers expect to be applying predictive modelling to a variety of claim issues, particularly for individual and systemic potential fraud detection. Predictive modelling is already an important pricing tool for P&C insurers and is progressing toward much wider and deeper uses. Among the reasons, according to the Towers Watson survey, are greater pricing accuracy, improved loss ratios and increased profitability. Insurers are using it to better understand current and future insured risks, resulting in improved risk segmentation, underwriting, pricing, claim and marketing decisions. Advanced applications in the areas of price optimization and telematics are reinforcing the importance of this powerful tool.
|