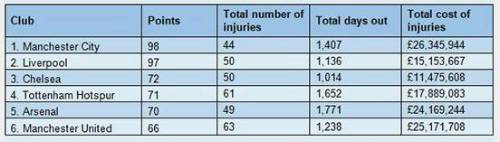
A likely consequence of the 2018 FIFA World Cup, player fatigue, and shortening summer recovery times, the busiest physio table belonged to Manchester United, with 63 injuries, while Wolves experienced the lowest number of injuries (11) last season.
The Football Injury Index 2019, which is produced by Marsh JLT Specialty, asserts that the cost of injuries to Premier League clubs reached a record £221 million in 2018-19, a 3% rise on the 2017-18 season.
Manchester City incurred the highest injury costs in 2018-19, spending £26.3 million on injured players, but the clubs most affected by injuries throughout the season were West Ham (2,003 total days out), Arsenal (1,771 days out) and Tottenham (1,652 days out); these three clubs also topped the list for average unavailability of players each match day.
The rise in injury costs has largely been driven by the top six clubs, which account for 54% of these costs. The top six have experienced an average 48% increase in salaries paid to injured players since 2016, with Tottenham Hotspur particularly affected, seeing costs rise by 110% in the last three years.
Premier League injuries snapshot: top six analysis
Lennox Batten, Managing Director, Special Risks, Marsh JLT Specialty, commented: “As football’s popularity continues to rise, top level clubs have even more financial fire power and are using extra revenue to attract elite talent with higher wages in a highly competitive global marketplace.
“The 2018-19 season saw record levels of injuries in the Premier League, notably driven by an abnormally high number of injuries in August and December as a likely consequence of the 2018 World Cup, and a relentless footballing calendar.
“The fact that injury hit English clubs dominated European competitions last season illustrates just how elite clubs have the ability to continue competing through injury crises. However, with wages set to continue rising and the footballing calendar remaining as congested as ever, the cost of injuries - effectively the cost of doing business in the game - is likely to keep increasing in the long term.”
|

